Introduction to Compiler
- A compiler is a translator that
converts the high-level language into the machine language.
- High-level language is written
by a developer and machine language can be understood by the processor.
- Compiler is used to show errors
to the programmer.
- The main purpose of compiler is
to change the code written in one language without changing the meaning of
the program.
- When you execute a program
which is written in high level programming language then it executes into two
phases.
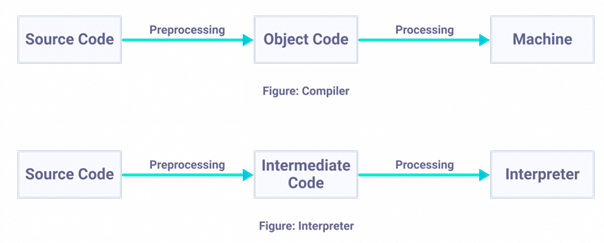
- In the first phase, the source
program compiled and translated into the object program (low level
language).
- In the second phase, object
program translated into the target program through the assembler.
Interpreter
Interpreter also
converts the high level language into machine readable binary equivalents. Each
time when an interpreter gets a high level language code to be executed, it
converts the code into an intermediate code before converting it into the
machine code. Each part of the code is interpreted and then execute separately
in a sequence and an error is found in a part of the code it will stop the
interpretation of the code without translating the next set of the codes.
Interpreter
Vs Compiler
|
Interpreter |
Compiler |
|
Translates program one statement at a time. |
Scans the entire program and translates it as a
whole into machine code. |
|
Interpreters usually take less amount of time
to analyze the source code. However, the overall execution time is
comparatively slower than compilers. |
Compilers usually take a large amount of time
to analyze the source code. However, the overall execution time is
comparatively faster than interpreters. |
|
No intermediate object code is generated, hence
are memory efficient. |
Generates intermediate object code which
further requires linking, hence requires more memory. |
|
Programming languages like JavaScript, Python,
Ruby use interpreters. |
Programming languages like C, C++, Java use
compilers. |


No comments:
Post a Comment